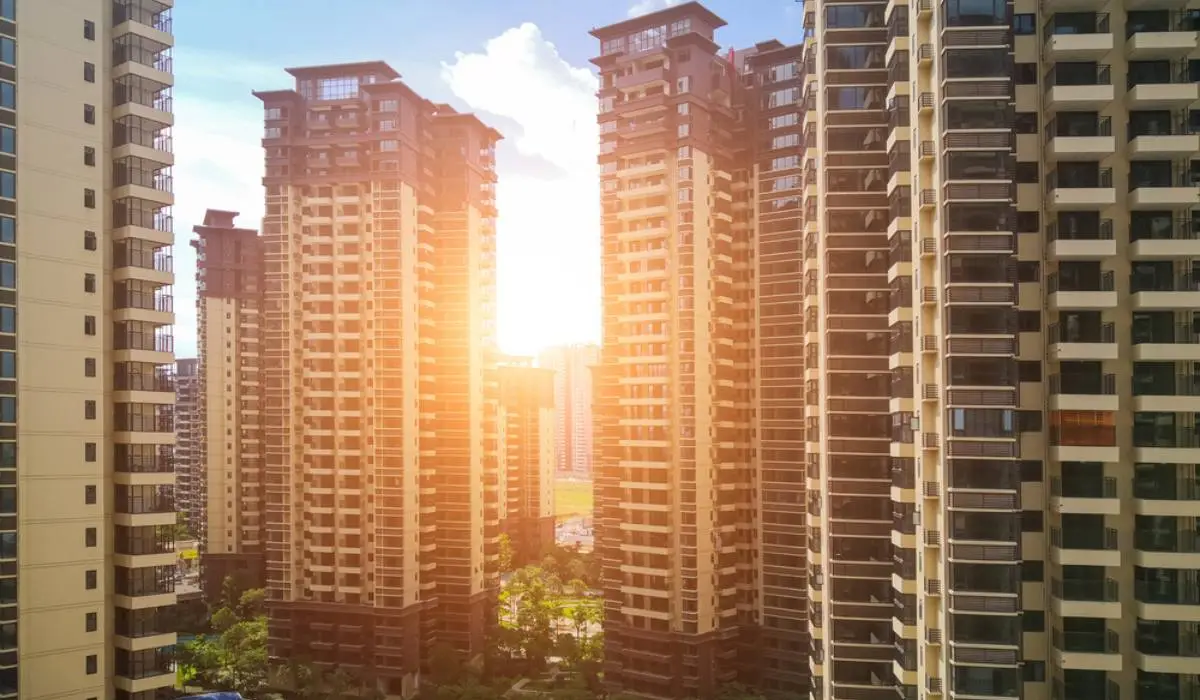
A multi-storey building is a vertical structure that consists of two or more floors (storeys) built one above the other. These buildings are designed to maximize land use by building upward instead of outward, and are used for residential, commercial, institutional, or mixed purposes.In simple words: Any building that has a ground floor and at least one more floor above it is a multi-storey building.
Characteristics of Multi-Storey Buildings
-
Multiple Floors
-
Has 2 or more floors built on top of each other.
-
The total number of storeys depends on the purpose and the building design.
-
-
Vertical Movement Systems
-
Contains stairs, elevators (lifts), and sometimes escalators to move people between floors.
-
High-rise buildings require multiple lifts and emergency staircases.
-
-
Structural Framework
-
Built using Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC), steel, or a combination.
-
Must be strong enough to carry the vertical load (weight of floors) and lateral forces (like wind and earthquake).
-
-
Efficient Land Use
-
Maximizes the use of limited land space, especially in urban cities.
-
Helps accommodate more people or businesses on a smaller land parcel.
-
-
Common Utilities
-
Centralized systems for water supply, drainage, electricity, fire safety, and waste management.
-
Larger buildings may have backup power, intercom, CCTV, etc.
-
-
Zoning and Safety Compliance
-
Must follow government rules related to height restrictions, fire escape routes, and earthquake resistance.
-
-
Amenities
-
Often come with shared spaces like parking, garden, gym, rooftop space, children’s play area, etc.
-
Types of Multi-Storey Buildings
1. Low-Rise Buildings
-
2 to 4 floors
-
Mostly residential
-
No elevator required (staircase is enough)
-
Common in suburban or smaller towns
2. Mid-Rise Buildings
-
5 to 10 floors
-
Common in growing urban areas
-
Usually has elevators and fire systems
-
Mixture of residential and office use
3. High-Rise Buildings
-
11 to 40 floors
-
Advanced structural engineering required
-
Mandatory fire exits, multiple lifts, and earthquake-resistant design
4. Skyscrapers / Super High-Rise
-
40+ floors, sometimes reaching up to 100+ floors
-
Seen in metro cities or international business hubs (e.g., Mumbai, Dubai, New York)
-
Require highly specialized design, HVAC systems, and automation
Uses of Multi-Storey Buildings
-
Residential: Apartments, condominiums, hostels
-
Commercial: Corporate offices, IT parks, shopping complexes
-
Mixed-use: Shops on lower floors, homes or offices on top floors
-
Institutional: Hospitals, colleges, hotels
Advantages of Multi-Storey Buildings
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficient Land Use | More people/accommodation in limited land space |
| Cost Effective (per unit) | Cost per flat or office can be lower due to shared land |
| Modern Amenities | Facilities like lift, parking, power backup, etc. |
| Better Ventilation & View | Higher floors get better air circulation and less noise |
| Community Living | Apartments promote social interaction and security |
| Revenue Potential | Builders or owners can lease out multiple units for income |
Relevance in Modern Cities
Multi-storey buildings are the backbone of urban development. In land-scarce cities like Chennai, Mumbai, Bengaluru, high land costs make it impractical to build horizontal houses. Multi-storey buildings:
-
Accommodate growing populations
-
Support infrastructure like metro stations, schools, hospitals nearby
-
Allow developers to offer modern lifestyle amenities
A multi-storey building is not just a structure with many floors. It’s a smart architectural and engineering solution to modern urban challenges. With proper design, amenities, and safety measures, they provide convenient, affordable, and sustainable living or working spaces for the future.
https://www.livehomes.in/blogs