What is RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) Construction?
Meaning:
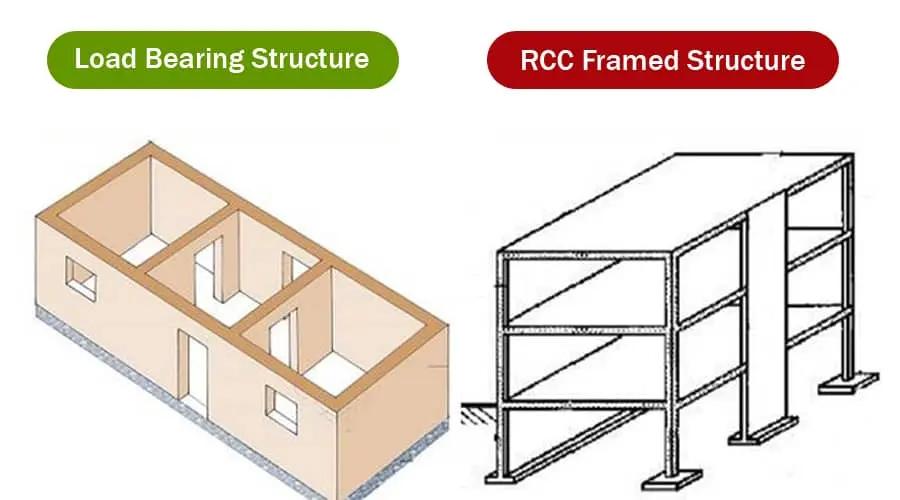
RCC construction uses cement concrete + steel rods to make the main structure strong and durable. The building’s load (weight) is carried by columns, beams, and slabs — not by the walls.
How it works:
-
Columns: Vertical supports that carry weight from the top to the foundation.
-
Beams: Horizontal members that support the roof/floor and pass the load to the columns.
-
Slab: The flat part (floor/ceiling) where people walk or place furniture.
-
Steel rods inside the concrete make it strong and flexible during earthquakes or pressure.
Where it’s used:
-
High-rise apartments
-
Commercial buildings
-
Hospitals, malls, offices
-
Modern houses
Advantages:
-
You can build multi-storey buildings (3, 5, 10, even 50 floors).
-
Walls are not load-bearing, so you can change room layout later.
-
Stronger and earthquake-resistant.
-
Modern look and design flexibility.
-
More open space possible (larger halls, fewer walls).
Disadvantages:
-
Costlier than load-bearing
-
Requires skilled engineers and labor
-
More time and machinery needed
What is Load Bearing Construction?
Meaning:
In this method, the walls carry the total load of the building — including floors and roof. There are no columns or beams. Walls are built thicker to support the building’s weight.
How it works:
-
The building's weight is directly passed from the roof/floor to walls, and from walls to the foundation.
-
Mostly uses brick or stone masonry.
How it works:
-
The building's weight is directly passed from the roof/floor to walls, and from walls to the foundation.
-
Mostly uses brick or stone masonry.
Where it’s used:
-
Small houses
-
Ground + 1 or Ground + 2 buildings
-
Rural areas or old-style construction
Advantages:
-
Low cost – ideal for small buildings
-
Simple to build
-
Doesn’t require advanced engineering
-
Good for small plots or independent homes
Disadvantages:
-
Not suitable for tall buildings
-
Walls must be thick, so less usable space inside
-
Difficult to modify walls later
-
Not earthquake-resistant in most cases
Key Differences Table:
| Feature | RCC Construction | Load Bearing Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Structure Support | Columns and Beams | Thick Walls |
| Number of Floors Supported | Multiple floors (3+ and high-rise) | Limited (usually up to 2 floors) |
| Design Flexibility | High – can change wall layouts | Low – walls cannot be altered easily |
| Earthquake Resistance | Good (if designed well) | Poor |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Time to Build | More time (complex process) | Less time (simple structure) |
| Interior Space | More usable space | Less space due to thick walls |
Real-Life Example:
-
RCC: Modern apartments in cities like Chennai, Bengaluru, Mumbai.
-
Load Bearing: Old independent houses or village homes made of red bricks or stones.
-
If you are building a small, low-budget home, load-bearing might work.
-
If you want a multi-floor, strong, and modern home/apartment, RCC is the best choice.
https://www.livehomes.in/blogs